Standard Treatment Guidelines
Standard Treatment Guidelines play critical role in ensuring evidence based clinical practice and quality of care. Taskforce on Standard Treatment Guidelines Have worked towards developing evidence based clinical guidelines and implementation tools.
Standard Treatment Guidelines, also termed as clinical guidelines and clinical protocols are component of health services provisioning to ensure evidence based medicine and quality of care. At health system level it helps in planning and costing of services. Standards Treatment Guidelines also become important tool for monitoring and authorising procedure in a public funded health insurance schemes. With this quality control, regulatory and planning functions standard treatment guidelines become indispensable tools both for public and private service providers
Understanding its importance, Ministry of Health & Family welfare commissioned a Taskforce on Standard Treatment Guidelines Which comprised of eminent clinicians and representations from important stakeholders such as ICMR, DGHS , FICCI, civil society organizations and academic institutions. NHSRC was designated as secretariat for this taskforce. The objective of this taskforce was to collate and review the existing standards treatment guidelines as well as identify the procedures/ conditions where fresh development of Standard treatment Guidelines is required. Taskforce was also mandated to suggest principles / protocols by which guidelines are reviewed and updated. Taskforce was also asked to update the existing guidelines and companion documents aimed at treating doctors, insurance program teams, patients and clinical reviewers/ medical auditors.
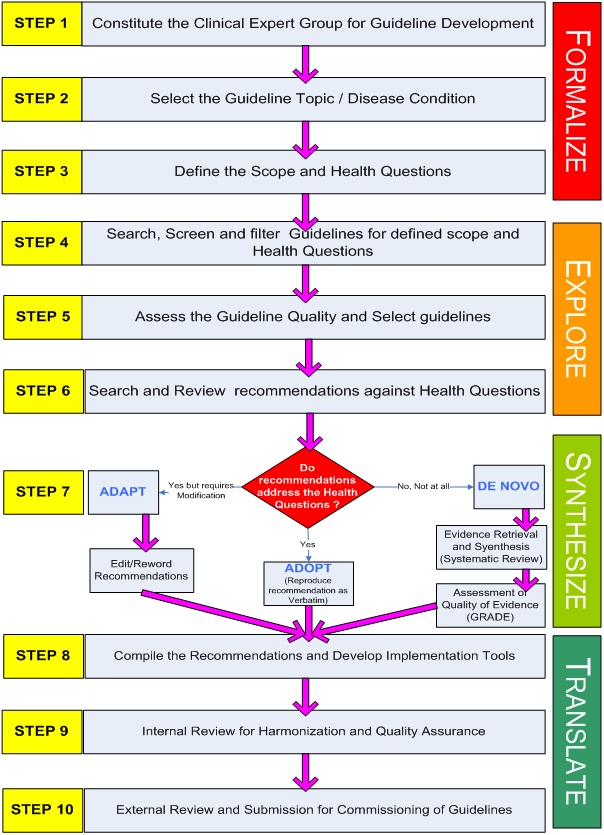
Process of STG Development
STG writing group
Taskforce decided to work on limited no. of guidelines in the first phase. 10 clinical specialty subgroups were formed with each group initially to focus one disease condition. To make guideline group multidisciplinary each group was directed to recruit members from diverse background apart from domain experts. This includes allied health workers (Nursing/Paramedic/Rehabilitation), Physician, private practitioners, primary care doctors, public health/ health system experts, methodology experts and patients or patients right organization. In each the senior most expert was usually designated as facilitator. Each member was asked to declare any conflict of interest on a standardized format and records are kept with Taskforce secretariat. Writing group members were trained for the guideline development methodology in a two day workshop with technical support of NICE, UK. Each subgroup was allocated some financial resources by NHSRC for conducting subgroup meetings and covering other incidental cost.
Topic Selection Process
Each subgroup was requested to propose 5 disease conditions of their respective clinical specialty. These disease conditions were prioritized on a criteria based on burden of disease, non availability of Indian guidelines and policy importance. The disease conditions on which MoHFW already have issued guidelines were excluded. Total 14 disease condition Were, selected for the first phase.
Guideline Development
Guidelines were developed using agreed ‘Hybrid’ methodology adopting/adapting guidelines as explained above. Scope of Guidelines was defined before starting the search for guidelines. As a strategy reputed repositories of guidelines such National Guideline Clearinghouse and NICE were searched for existing guidelines as these have been already screened for quality. For guidelines from other sources a screening of guidelines against AGREE II tool was done before considering them for adoption/adaption.
Documentation
Once the recommendations were finalized (Adopted or Adapted) following documents were developed.
Full Background document
Contains the detailed recommendations along with reference to source guidelines. Document also describes the process of development of guideline, details of writing group members, and decision taken on adopting or adapting on specific recommendations.
Quick Reference Guide
A concise version of full document consists of key recommendations and clinical pathways more targeted for frontline clinicians.
Apart from these, implementation tools such as Quality Standards, Patient Information Sheet and Formulary were also developed for each set of guidelines.
Review Process
All the documents went through three tier review process. First Internal review was done by a designated internal harmonization group. This group reviewed the document for consistency and adherence to agreed methodology. Once the internal review suggestions were incorporated documents were submitted to DGHS for external review, who in turn appointed prominent expert for external review of the documents. Finally documents were uploaded on MoHFW and NHM website for one month for open consultation and comments from public. Finally revised documents were submitted to MoHFW for final approval and commissioning.